High-Pressure Sensors for Oil & Chemical Plants: A Comprehensive Guide
Operating oil and chemical plants means working right up against the limits of heat, pressure, and volatile media—and that’s exactly why dependable high-pressure sensors are non-negotiable. When the instrumentation is solid, safety improves, processes run smoother, and compliance stays on track. I’ve had nights where a tiny pressure drift flagged by a good transmitter saved a unit from an emergency shutdown; those moments stick with you and underscore how crucial it is to understand the sensors, their certifications, and how to match them to each application.
Why Reliable High-Pressure Sensors Are Crucial in Oil and Chemical Facilities
1. Understanding the inherent risks and challenges of high-pressure environments
Oil and chemical plants routinely work with volatile fluids under intense pressure and extreme temperatures. That combination raises the stakes: explosions, leaks, and equipment failures are ever-present risks. A sudden spike or dip in pressure can cascade into a serious incident, putting people and the environment in harm’s way. That’s why continuous, accurate pressure monitoring is a foundational safeguard. The overall integrity of plant operations rests heavily on the reliability of the sensing equipment.
2. The impact of inaccurate pressure measurement on safety and operational efficiency
Poor pressure data can have outsized consequences. From a safety standpoint, small deviations can snowball into major hazards, prompting emergency trips or uncontrolled releases. From an operations perspective, bad data breeds inefficiency: wasted energy, off-spec product, and avoidable rework. Consider a distillation column—keep pressure on point and you protect separation efficiency and yield; lose precision and operators are flying blind, forced into guesses that sap performance and raise costs.
3. Regulatory compliance and industry standards for pressure monitoring
These industries are tightly regulated for good reason. Bodies such as API, OSHA, and IEC set rigorous standards for equipment selection, installation, and operation—including pressure monitoring systems. Compliance isn’t optional; it’s the baseline for safety and environmental stewardship. Falling short risks fines, shutdowns, and reputational damage. High-pressure sensors must carry the right certifications to be accepted for use in these hazardous applications.
Exploring the Technology Behind High-Pressure Sensors
1. Different types of high-pressure sensing technologies and their working principles
A few core technologies dominate high-pressure measurement, each with its own strengths. Piezoresistive sensors exploit resistance changes in a material under mechanical stress, delivering high accuracy and stability. Capacitive sensors measure the change in capacitance between plates as one flexes under pressure. Ceramic Pressure Sensors bring excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for aggressive media. Silicon pressure sensors, often using diffused piezoresistive silicon elements, deliver high sensitivity and repeatability.
2. Key features and specifications of high-pressure transmitters for hazardous areas
Transmitters destined for hazardous areas need purpose-built protection: rugged, explosion-proof housings, intrinsically safe designs, and approvals such as ATEX or IECEx. Performance-wise, look for wide measurement ranges, high accuracy (e.g., ±0.05% FS), and strong long-term stability. Integrated temperature compensation helps the transmitter stay precise as process temperatures swing. For integration, digital outputs like RS485 Modbus RTU are common and make life easier for controls teams.
3. Material selection and construction for corrosion resistance and durability
Aggressive media in oil and chemical service demand careful materials engineering. Stainless steel such as SUS316L is a go-to for corrosion resistance, while more severe environments call for alloys like Hastelloy or Monel. The diaphragm—the wetted surface that sees the process directly—often uses ceramic or exotic metals to withstand chemical attack and elevated temperatures. A robust mechanical design pays off in longevity and fewer failures. If you’re interested, check 《Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors vs. Ceramic Pressure Sensors: A Comprehensive Comparison》.
Critical Applications of High-Pressure Sensors in Oil and Chemical Plants
1. Monitoring and control in upstream and downstream oil and gas operations
Upstream, high-pressure sensors keep watch over wellhead pressures, drilling mud systems, and pipeline integrity—environments with extreme pressures and corrosive fluids. Downstream in refineries and processing units, they’re essential on catalytic crackers, hydrotreaters, and fractionators to maintain efficiency and guard against overpressure conditions. In both arenas, accurate pressure data directly supports process control and safety.
2. Pressure management in chemical processing and petrochemical facilities
Chemical processing spans countless reactions and separations, many at high pressure. Sensors regulate reactor pressure to keep reactions safe and efficient, and they track pipeline pressures for feeds and products to prevent leaks and maintain steady flow. The chemical sector relies on these measurements for tight control of critical parameters—protecting product quality and plant safety in equal measure.
3. Ensuring safety in critical infrastructure and storage tanks
Storage tanks holding flammable or toxic chemicals must avoid both over-pressurization and vacuum conditions, which can cause rupture or collapse. High-pressure sensors mounted on tanks and connected lines provide real-time feedback to control systems so corrective actions can be taken early. In these critical services, sensor reliability isn’t just desirable—it’s essential to protect infrastructure and the environment.
Selecting the Right High-Pressure Sensor for Your Industrial Needs
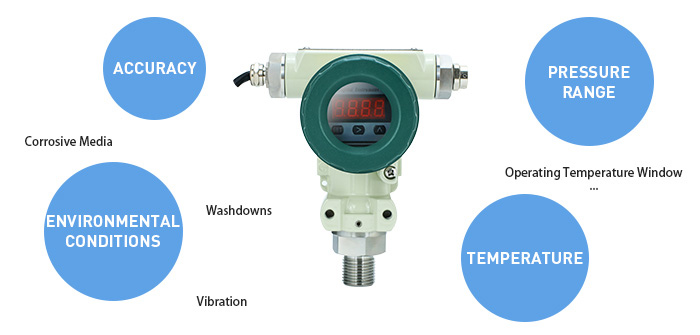
1. Factors to consider: pressure range, accuracy, temperature, and environmental conditions
Selecting the right sensor starts with a clear spec. Define the pressure range, including normal operation and foreseeable excursions. Match accuracy to the process need—tighter accuracy typically improves control and safety margins. Confirm the operating temperature window and how extremes might affect performance and life. Then weigh environmental factors: corrosive media, vibration, washdowns, or hazardous atmospheres, all of which influence the right build and protection level.
2. The importance of certifications (e.g., ATEX, CE, ISO, RoHS) for hazardous locations
In hazardous locations, certifications like ATEX (Europe), IECEx (international), and local explosion-proof approvals are must-haves. They confirm the device is designed and tested not to ignite explosive atmospheres. CE marking speaks to European safety, health, and environmental compliance; ISO certifications indicate mature quality systems; and RoHS restricts hazardous substances in electronics. Selecting certified hazardous area sensors is a critical step for safety. We recommend reading Safety in Hazardous Areas: Using Explosion-Proof Sensors for more details.
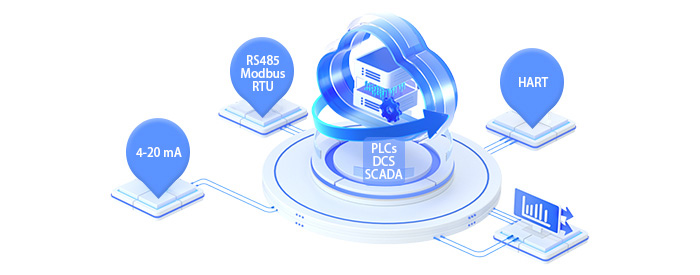
3. Integration with existing control systems and communication protocols (e.g., Modbus RTU)
Clean integration is key. Modern high-pressure sensors support common plant protocols like 4-20 mA, HART, and RS485 Modbus RTU, ensuring reliable links to PLCs, DCS, or SCADA systems. We make sure our sensors offer flexible I/O so installation is straightforward and data flows smoothly across complex networks—minimizing downtime and simplifying lifecycle maintenance.
The Benefits of Partnering with an Experienced Sensor Solution Provider
1. Custom solutions and OEM/ODM support for unique application requirements
Some applications simply don’t fit off-the-shelf. An experienced provider can tailor designs—custom ranges, wetted materials, packaging, or environmental protections—to match the duty. With OEM/ODM support, the result is a sensor that fits the process like a glove and performs reliably over time. We collaborate closely with clients to turn requirements into integrated, field-ready solutions.
2. Ensuring long-term reliability and performance through quality manufacturing
Long-term accuracy and stability start with disciplined manufacturing: high-grade materials, tight process controls, and thorough inspection. Trustworthy providers live this every day, from early design decisions through final test. That consistency reduces recalibration frequency, cuts maintenance costs, and keeps plants running. Our quality focus is embedded in every stage of production.
3. Comprehensive pre-sales and after-sales support for seamless implementation
Good support smooths every step. Up front, we help evaluate applications and recommend the right sensor builds. After purchase, we stand behind installation, calibration, and troubleshooting to keep operations steady. With strong pre- and post-sales support, plants can implement pressure monitoring cleanly and sustain performance over the long haul. We aim to make it genuinely one-stop and worry-free.

Partner with Pokcenser Automation for Your High-Pressure Sensor Needs
At Pokcenser Automation, we’ve built our reputation around the safety and efficiency high-pressure sensors bring to oil and chemical plants. Our portfolio of robust pressure transmitters and industrial sensors is designed for harsh service and backed by hard-won application expertise. Reach out to discuss your requirements—our tailored solutions are built to elevate reliability and performance. We’re committed to creating real value for clients worldwide.
Phone: +86 181 7515 5326
Email: in**@*******er.com
About the Author
Li Chengxuan is a senior industrial automation expert at Pokcenser Automation, specializing in the research and application of flow, level, pressure and temperature sensors and industrial process control solutions.
FAQs
1. What are the primary risks associated with high-pressure environments in oil and chemical plants?
Explosions, toxic leaks, and equipment failures are the principal hazards, driven by volatile substances and the extreme temperatures and pressures needed to process them.
2. How do high-pressure sensors contribute to operational safety and efficiency?
They deliver real-time, accurate measurements that catch anomalies early and help prevent catastrophic events. On the efficiency side, precise data tightens process control, trims energy use, and stabilizes product quality.
3. What certifications should I look for when selecting high-pressure sensors for hazardous areas?
Prioritize ATEX and IECEx, along with applicable local explosion-proof approvals. These attest that the sensor meets stringent safety requirements for potentially explosive atmospheres.
4. Can high-pressure sensors be integrated with existing plant control systems?
Yes. Most modern devices support 4-20 mA, HART, and RS485 Modbus RTU, enabling straightforward connectivity with PLCs, DCS, and SCADA platforms.
5. What kind of maintenance do high-pressure sensors require?
Plan for periodic calibration to maintain accuracy. Add routine visual inspections for damage or corrosion and occasional cleaning of the sensing element to support long-term reliability.
 English
English Spanish
Spanish
