8 Points about High Temperature Thermal Mass Flow Meter You Must Know
In industrial processes where gases flow at elevated temperatures, accurate flow measurement becomes both critical and challenging. High temperature thermal mass flow meters have emerged as the preferred solution for applications ranging from combustion monitoring to chemical processing, offering reliable performance where conventional flow meters fail.
This comprehensive guide explores the technology, applications, and best practices for implementing thermal mass flow meters in high temp environments, helping engineers and plant managers make informed decisions for their demanding measurement needs.
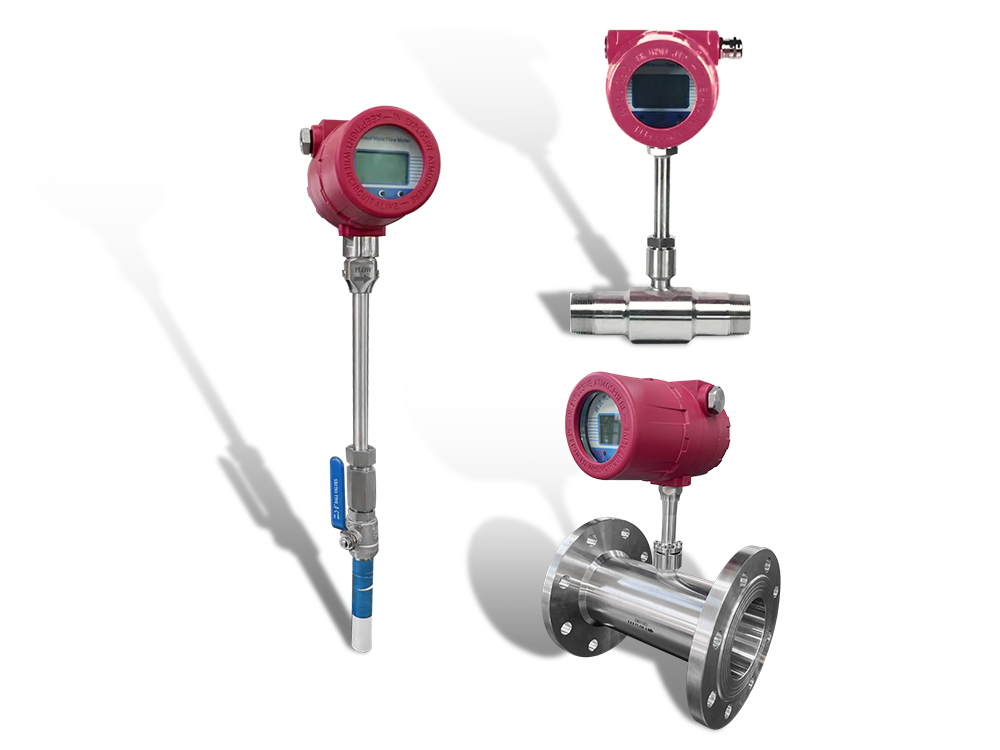

Figure 1. Product range of high-temperature thermal mass flow meters — available in insertion, inline, and flange-mounted designs for industrial gas applications.
High Temperature Thermal Mass Flow Meter Technology
Thermal mass flow meters operate on the principle of heat transfer, using heated sensor elements to directly measure mass flow rate of gases. Unlike volumetric flow meters that require pressure and temperature compensation, these devices provide true mass flow measurement regardless of changing process conditions—a critical advantage in high-temperature applications where gas density varies significantly.
The technology employs two temperature sensors: one heated element maintained at a constant temperature differential above the gas stream, and one reference sensor measuring actual gas temperature. As gas flows past the heated sensor, it carries away heat. The energy required to maintain the temperature differential directly correlates with the mass flow rate. This thermal dispersion flow meter principle remains effective even at extreme temperatures, provided the sensor materials and electronics are properly engineered for thermal resilience.
How High Temperature Capability is Achieved
Standard thermal mass flow meters typically operate to 200-250°C, but high temp mass flow meters extend this range dramatically—often to 500°C, 650°C, or even 850°C depending on design and materials. This capability requires several engineering innovations:
Advanced sensor materials including high-temperature alloys, ceramic insulators, and specialized heating elements that maintain stability at elevated temperatures without degradation. Inconel, Hastelloy, and high-grade stainless steels commonly form the wetted components, while electronics are thermally isolated or remotely mounted.
Thermal barrier designs physically separate sensitive electronics from the hot process environment. Extended sensor stems, heat sinks, and active cooling systems protect measurement circuitry while allowing sensor tips to withstand process temperatures. Some designs place all electronics in remote transmitters connected via high-temperature cables.
Specialized calibration procedures account for thermal effects on sensor characteristics across the entire operating temperature range, ensuring measurement accuracy remains within specification whether measuring ambient air or 600°C flue gas.
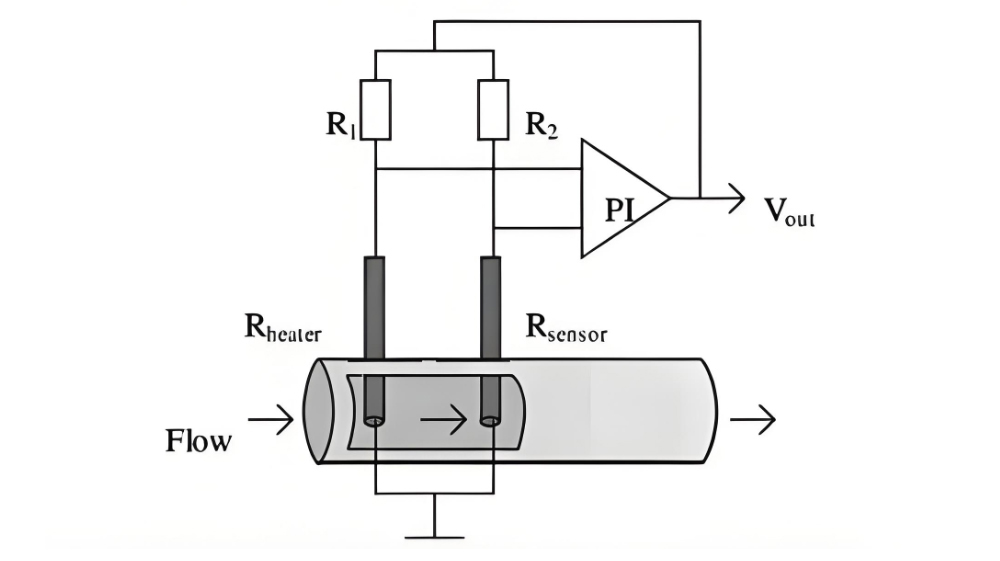
Figure 2. Working principle of a thermal mass flow meter — using heated and reference sensors to measure gas mass flow through thermal dispersion.
Key Advantages for High-Temperature Applications for Temperature Thermal Mass Flow Meter
Direct Mass Flow Measurement
Industrial thermal mass flow meters measure what matters most—actual mass flow. In high-temperature processes where gas density can vary by 50% or more compared to ambient conditions, volumetric measurements require complex compensation calculations. Mass flow meters eliminate this complexity, providing readings directly usable for combustion control, process optimization, and material balance calculations.
No Moving Parts, Minimal Pressure Drop
The thermal flow meter hot gas design typically features no mechanical components in the flow stream. This eliminates concerns about bearing failures, rotor damage, or mechanical wear in harsh environments. The obstruction-free path creates negligible pressure drop—crucial in draft-sensitive applications like flue gas monitoring or furnace air flow measurement.
Wide Measurement Range
High temperature gas flow meters typically offer turndown ratios of 100:1 or greater, accurately measuring from very low velocities up to maximum rated flows. This exceptional rangeability accommodates varying process conditions without requiring multiple meters or frequent recalibration. A single meter handles startup, normal operation, and peak demand conditions effectively.
Installation Flexibility
Available in both inline (full-bore) and insertion-style configurations, these meters adapt to existing piping infrastructure. Insertion models allow hot-tap installation in large ducts without process shutdown—particularly valuable in continuous operations like power generation or steel manufacturing where downtime costs are prohibitive.
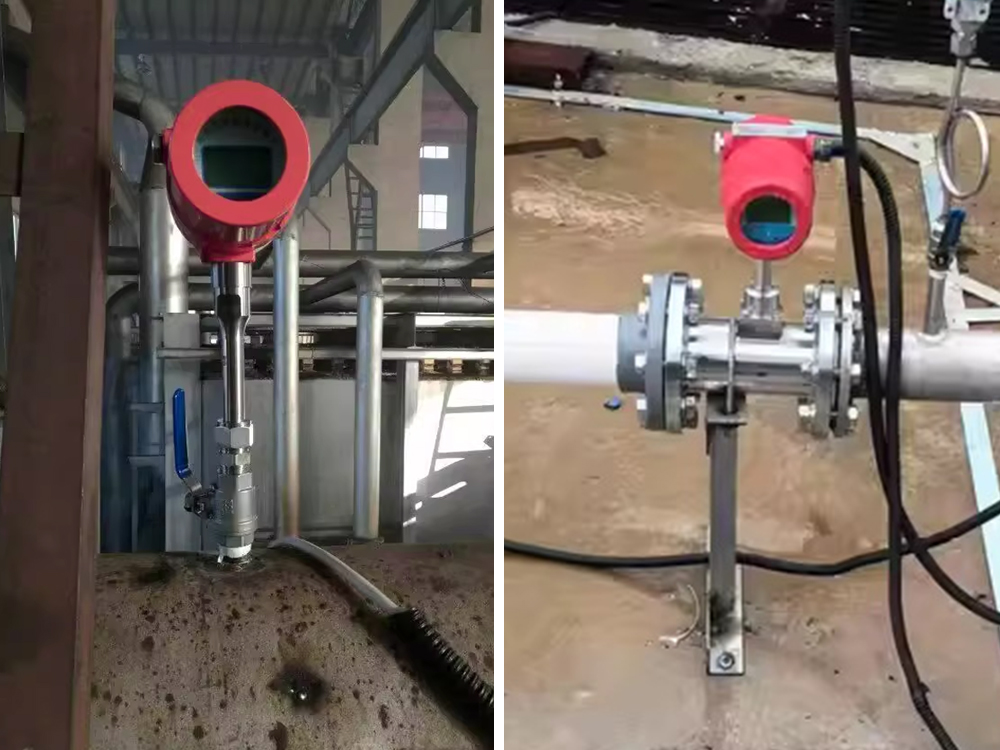

Figure 3. Real-world installation of high-temperature thermal mass flow meters in industrial plants for combustion air and exhaust gas monitoring.
Explore our range of high-temperature thermal mass flow meters designed for your specific application. Download our free selection guide with performance curves and application examples.
Critical High-Temperature Applications for Temperature Thermal Mass Flow Meter
Combustion Air and Flue Gas Monitoring
Thermal mass flow sensors high temperature excel in combustion applications where accurate air-fuel ratio control directly impacts efficiency and emissions. Measuring combustion air flow entering burners and flue gas exiting stacks—often at 400-600°C—these meters enable precise control systems that optimize fuel consumption while minimizing NOx, CO, and particulate emissions.
Power plants, industrial boilers, and process heaters rely on thermal mass flow meters for continuous emissions monitoring systems (CEMS) compliance and efficiency optimization. The meters’ ability to measure low velocities accurately makes them ideal for large ducts where traditional technologies struggle.
Petrochemical and Refining Processes
Catalytic cracking, reforming, and other high-temperature petrochemical processes require reliable flow measurement for process control and safety. High temp mass flow meters monitor hydrogen, nitrogen, steam, and hydrocarbon gases at temperatures reaching 500°C or higher. Their corrosion-resistant materials withstand aggressive chemical environments while maintaining measurement integrity.
Flare gas monitoring, thermal oxidizer control, and reactor feed gas measurement benefit from the thermal meter’s fast response time and high accuracy. Safety-critical applications depend on their proven reliability in demanding conditions.
Steel and Metal Production
Steel mills, aluminum smelters, and metal foundries operate furnaces and heat treatment equipment at extreme temperatures. Thermal flow meters for high temperature applications measure blast furnace gases, annealing atmosphere flows, and cooling air distribution. These measurements optimize energy consumption, improve product quality, and enhance process safety.
The meters’ rugged construction withstands the particulate-laden, high-temperature, and vibration-rich environments typical of metal production facilities. Many installations exceed 10 years of continuous operation with minimal maintenance.
Glass Manufacturing
Glass melting furnaces operate at temperatures exceeding 1500°C, with combustion air and waste gas flows requiring precise measurement and control. Industrial gas flow meters high temperature variants designed for glass industry applications handle the extreme thermal conditions, providing the data necessary for fuel efficiency optimization and emission compliance.

Figure 4. Major industries using high-temp thermal mass flow meters — power, petrochemical, steel, and glass sectors requiring accurate hot gas flow measurement.
Technical Specifications and Performance Criteria for Temperature Thermal Mass Flow Meter
Temperature Range and Limitations
High temperature thermal mass flow meters are classified by maximum process temperature capability:
- Standard high-temp: 250-400°C for general industrial applications
- Extended range: 400-650°C for demanding processes like flue gas and reformer off-gas
- Extreme temperature: 650-850°C for specialized applications including glass furnace exhaust
Beyond the sensor temperature rating, ambient conditions at the electronics location must be considered. Remote-mount configurations separate heat-sensitive components from the process, extending application possibilities.
Material Selection
Wetted materials must withstand not only temperature but also chemical exposure and thermal cycling. Common choices include:
- 316/316L stainless steel: Standard choice for temperatures to 400°C with non-corrosive gases
- Inconel 600/625: Superior high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance to 650°C
- Hastelloy C-276: Maximum corrosion resistance for aggressive chemical environments
- Ceramic sensors: Specialized designs for extreme temperatures exceeding 800°C
Sensor element materials (typically platinum or tungsten) are selected for stable thermal properties and resistance to contamination across the operating temperature range.
Accuracy and Repeatability
Quality thermal mass flow meter high temp instruments achieve accuracy of ±1% to ±2% of reading over a wide flow range, with repeatability typically ±0.5% of reading. This performance level supports critical process control and regulatory compliance requirements.
Accuracy specifications should always reference operating conditions including temperature, pressure, and gas composition. Some meters offer enhanced accuracy through multi-point calibration or built-in temperature compensation algorithms.

Figure 5. Calibration and inspection of a high-temperature thermal mass flow meter ensuring measurement accuracy and long-term performance.
Selection Considerations for High-Temperature Applications
Gas Properties and Composition
Thermal mass flow meters are gas-specific; accuracy depends on the measured gas’s thermal properties. Hot gas flow measurement applications require knowing the gas composition, as mixtures require special calibration or correction factors. Some advanced meters feature multi-gas calibration tables or can accommodate varying compositions through real-time correction.
Water vapor content significantly affects thermal measurements, particularly in combustion gases. Wet gas corrections or condensate removal may be necessary depending on moisture levels and temperature.
Pipe Size and Flow Velocity
Insertion-style meters suit large pipes and ducts (typically 2 inches to 10+ feet diameter) where inline meters would be prohibitively expensive. However, velocity must remain within the meter’s specified range—typically 0.25 to 100 meters per second (50 to 20,000 feet per minute). Very large ducts may require multiple insertion points for accurate flow profiling.
Inline meters provide superior accuracy in smaller pipes (½ inch to 12 inches) where full flow profile measurement is feasible. They’re preferred for critical measurements requiring highest accuracy and regulatory approval.
Installation Environment
Environmental factors influence meter selection and installation design:
- Vibration: Industrial environments may require vibration-isolated mounting or ruggedized sensor construction
- Ambient temperature: Electronics ratings must accommodate the installation location’s thermal conditions
- Hazardous areas: Explosion-proof or intrinsically safe designs comply with ATEX, IECEx, or NEC requirements
- Accessibility: Maintenance requirements dictate placement for periodic cleaning, calibration verification, or sensor replacement
Uncertain which high-temperature flow meter suits your application? Our application engineers provide free technical assessments including sizing calculations and installation recommendations. Contact us now.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices of Temperature Thermal Mass Flow Meter
Proper Installation Techniques
Thermal mass flow meter performance depends heavily on correct installation. Key requirements include:
- Straight pipe runs: Minimum 10 diameters upstream and 5 diameters downstream for inline meters; insertion meters may require 20+ diameters depending on flow disturbances
- Probe positioning: Insertion meters must be positioned according to manufacturer specifications, typically at specific depths for optimal flow profile measurement
- Orientation: Many designs require specific mounting orientation (horizontal, vertical, or any position depending on model)
- Thermal isolation: Protect electronics from excessive radiant or conducted heat using heat shields, extended mounting, or remote configurations
Calibration and Verification
Initial calibration at the factory establishes baseline performance using certified flow standards and the actual process gas when possible. Field verification should occur:
- After installation: Confirm proper operation before commissioning
- Annually or per regulations: Many applications require periodic calibration verification
- After maintenance: Any sensor removal or replacement necessitates verification
- When performance questions arise: Trending data may indicate drift requiring attention
Some high temperature thermal mass flow meters feature self-diagnostic capabilities that continuously monitor sensor function, alerting operators to potential issues before accuracy degrades significantly.
Maintenance Requirements
Thermal mass flow meters are relatively low-maintenance compared to mechanical alternatives, but high-temperature applications present unique challenges:
Sensor fouling from particulates, condensates, or chemical deposits degrades performance. Periodic cleaning may be required in dirty gas applications. Removable sensors simplify maintenance, though process shutdown or isolation is typically necessary.
Thermal cycling stresses materials and joints. Regular inspection for cracks, loosened fittings, or insulation degradation prevents failures. High-cycle-count applications may require more frequent sensor replacement.
Electronics protection ensures long service life. Verify that junction boxes remain sealed, cable entries intact, and cooling systems (if present) operational. High ambient temperatures accelerate electronic component aging.
Industry Standards and Certifications of Temperature Thermal Mass Flow Meter
Industrial thermal mass flow meters for high-temperature service typically comply with:
- ISO 14511: International standard for thermal mass flow meters
- ASME MFC-20G: Performance requirements for gas thermal mass flow meters
- AGA Report No. 10: Natural gas application guidelines (when applicable)
- ATEX/IECEx: Explosion protection for hazardous area installations
- SIL certification: Safety integrity level ratings for critical safety applications
Compliance with relevant standards ensures the meter meets performance expectations and regulatory requirements for your specific application.
Conclusion
High temperature thermal mass flow meters represent proven, reliable technology for demanding industrial applications where other measurement methods struggle or fail entirely. Their ability to directly measure mass flow without moving parts, combined with extended temperature capabilities reaching 850°C, makes them indispensable tools in modern process industries.
Successful implementation requires understanding the measurement principle, carefully matching meter capabilities to application requirements, proper installation following best practices, and appropriate maintenance programs. When correctly specified and installed, these instruments deliver years of accurate, reliable service in the most challenging environments.
As industries push toward greater efficiency, tighter emissions control, and process optimization, the role of accurate hot gas flow measurement continues expanding. High temp mass flow meters provide the critical data enabling these improvements while withstanding conditions that would destroy conventional instrumentation.
Transform your high-temperature process monitoring with advanced thermal mass flow technology. Our engineering team brings rich experience in demanding applications from power generation to petrochemicals. Request your customized flow measurement solution today!
 English
English Spanish
Spanish
