Mastering Liquid Level Measurement with Differential Pressure Transmitters
Accurate liquid level measurement is crucial for operational efficiency and safety in numerous industries. In my experience, selecting the appropriate technology can significantly impact process control and resource management. Differential pressure transmitters offer a robust and reliable solution for these demanding applications. Understanding their principles, advantages, and selection criteria is essential for optimizing industrial processes.
Understanding the Challenges of Accurate Liquid Level Measurement
1. The Critical Need for Precision in Industrial Processes
Precise liquid level measurement is fundamental for maintaining product quality, ensuring safety, and optimizing production costs across various industries. In sectors such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and oil and gas, even minor inaccuracies can lead to significant financial losses, environmental hazards, or compromised product integrity. For instance, in a chemical reactor, maintaining exact liquid levels directly influences reaction kinetics and final product specifications. Overfilling can cause spills and safety risks, while underfilling can damage equipment or halt production.
2. Common Issues with Traditional Liquid Level Sensing Methods
Traditional liquid level sensing methods often present several limitations that hinder accuracy and reliability. Float switches, for example, can stick or corrode in certain liquids, leading to erroneous readings. Sight glasses offer direct visual indication but are prone to fouling, difficult to automate, and pose safety risks with hazardous fluids. Bubbler systems require a continuous air supply and can be sensitive to changes in liquid density or viscosity. These methods frequently demand more maintenance and may not provide the continuous, high-precision data required by modern industrial automation systems.
3. Factors Influencing Liquid Level Measurement Accuracy
Several factors can significantly influence the accuracy of liquid level measurements. These include variations in process temperature, which can alter liquid density and the volume of the tank itself. Pressure fluctuations within the vessel, especially in pressurized tanks, also affect readings. The presence of foam, turbulence, or agitation in the liquid can distort measurement signals. Additionally, the physical properties of the liquid, such as viscosity, corrosiveness, and the presence of suspended solids, dictate the suitability and performance of different sensor technologies.
How Differential Pressure Transmitters Measure Liquid Levels
1. The Fundamental Principle of Hydrostatic Pressure
Differential Pressure Meters measure liquid levels based on the principle of hydrostatic pressure. Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure exerted by a fluid at rest due to the force of gravity. This pressure is directly proportional to the height of the liquid column, its density, and the acceleration due to gravity. Consequently, by measuring the pressure at the bottom of a tank, one can infer the liquid level. This method is highly reliable as it directly correlates a physical property (pressure) to the desired measurement (level).
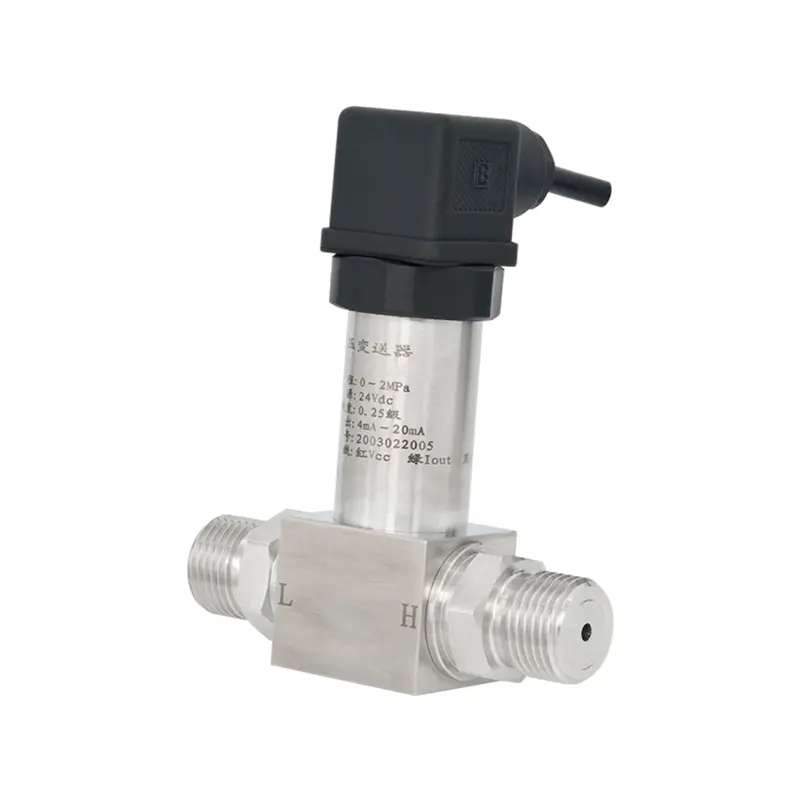
2. Components and Working Mechanism of a Differential Pressure Transmitter
A differential pressure transmitter typically consists of two pressure-sensing diaphragms, a fill fluid, and an electronic circuit. One side of the transmitter connects to the bottom of the tank to measure the total pressure (hydrostatic pressure plus any headspace pressure). The other side connects to the tank’s vapor space (for sealed tanks) or is vented to the atmosphere (for open tanks) to measure reference pressure. The transmitter then calculates the difference between these two pressures, which directly corresponds to the hydrostatic pressure exerted by the liquid column. This pressure difference is converted into an electrical signal, usually 4-20 mA or a digital output, representing the liquid level.
3. Types of Differential Pressure Transmitters for Various Liquid Applications
Different applications require specific types of differential pressure transmitters. For open tanks, a single-flange or direct-mount transmitter measures the hydrostatic pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. For closed or pressurized tanks, a dual-flange system is often used, with one flange at the bottom and another at the top, measuring the differential pressure across the liquid column. Remote seal systems are ideal for high-temperature or corrosive liquids, where the transmitter itself cannot be directly exposed to the process medium. These systems use capillary tubes filled with inert fluid to transmit pressure from the diaphragm seals to the transmitter.

Key Advantages of Using Differential Pressure Transmitters for Liquid Levels
1. Enhanced Accuracy and Repeatability in Diverse Conditions
Differential pressure transmitters offer superior accuracy and repeatability compared to many other level measurement technologies. Their measurement principle relies on a fundamental physical property, hydrostatic pressure, which provides consistent results even with minor process variations. Advanced sensor designs, including diffused piezoresistive silicon sensors, contribute to high precision and stability over long periods. This reliability is critical for processes demanding tight control and consistent product quality.
2. Robustness and Reliability in Harsh Industrial Environments
These transmitters are engineered to withstand demanding industrial conditions. Their robust construction and selection of corrosion-resistant materials allow them to operate reliably in environments with extreme temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive chemicals. Many models feature high IP ratings, ensuring protection against dust and water ingress. This durability minimizes downtime and reduces maintenance costs, contributing to a lower total cost of ownership. For applications in explosive atmospheres, explosion-proof sensors are available, ensuring safety and compliance.
3. Versatility Across Different Tank Geometries and Liquid Properties
Differential pressure transmitters adapt to a wide array of tank shapes and sizes, from tall, narrow vessels to wide, shallow sumps. They can measure levels in liquids with varying densities, viscosities, and even those containing suspended solids, provided the impulse lines are properly maintained. This versatility makes them a preferred choice for complex industrial setups where other technologies might struggle. Their ability to handle diverse liquid properties extends their applicability significantly.
4. Integration with Modern Industrial Automation Systems
Modern differential pressure transmitters seamlessly integrate with industrial automation systems. They typically provide standard output signals like 4-20 mA, HART, or various digital protocols (e.g., Modbus). This compatibility enables real-time data acquisition, remote monitoring, and advanced control strategies. Integration facilitates improved process visibility, automated decision-making, and enhanced overall operational efficiency.
If you’re interested, check 《8 Things You Should Know About Diffused Piezoresistive Silicon Sensors》.
Selecting the Right Differential Pressure Transmitter for Your Application
1. Evaluating Liquid Characteristics and Process Conditions
Selecting the optimal differential pressure transmitter begins with a thorough evaluation of the liquid characteristics and process conditions. Key considerations include the liquid’s density, viscosity, temperature range, and chemical compatibility with sensor materials. For instance, highly corrosive liquids require specialized wetted parts, while liquids prone to crystallization may need remote seals. Understanding the process pressure and temperature ranges is also vital for ensuring the transmitter’s survival and accuracy.
2. Considering Measurement Range, Accuracy, and Response Time
The required measurement range dictates the sensor’s pressure span. Accuracy specifications, often expressed as a percentage of full scale, determine the precision of the level readings. For critical applications, higher accuracy transmitters are necessary. Response time is another crucial factor, especially in dynamic processes where rapid level changes occur. A faster response ensures that the control system receives timely data for effective regulation.
3. Material Compatibility and Environmental Protection (IP Ratings, Certifications)
Material compatibility is paramount to prevent corrosion and ensure long-term reliability. Wetted parts must resist chemical attack from the process fluid. Environmental protection, indicated by IP ratings, specifies the degree of protection against dust and water. For harsh or hazardous environments, certifications like ATEX or IECEx are mandatory, ensuring the device meets stringent safety standards. These factors directly influence the longevity and safe operation of the transmitter.
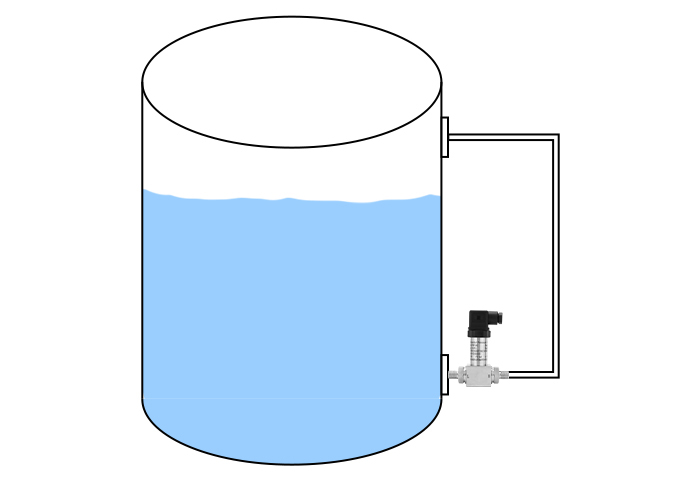
4. Output Signals and Communication Protocols for Seamless Integration
Modern differential pressure transmitters offer various output signals and communication protocols to facilitate seamless integration into existing control systems. Common analog outputs include 4-20 mA, while digital options often include HART, Modbus, or Foundation Fieldbus. The choice depends on the plant’s control architecture and data requirements. Digital protocols provide more diagnostic information and enable remote configuration, enhancing system intelligence and maintenance efficiency.

Practical Applications of Differential Pressure Transmitters in Industry
1. Tank Level Monitoring in Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
In chemical and petrochemical plants, precise tank level monitoring is critical for safety, inventory management, and process control. Differential pressure transmitters accurately measure levels in storage tanks, reactors, and distillation columns, even under high pressure or vacuum conditions. They handle a wide range of corrosive and volatile liquids, providing reliable data for automated systems. This ensures safe operation and prevents costly overfills or dry-runs.
If you’re interested, check 《Chemical Tanks》.
2. Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant Level Control
Water and Wastewater Treatment plants rely heavily on accurate level control for efficient operation. Differential pressure transmitters monitor levels in clarifiers, digesters, and filter beds. Their robust design withstands the demanding conditions of wastewater treatment and ensures consistent performance. This helps optimize chemical dosing, manage flow rates, and prevent system overflows, contributing to environmental compliance and operational stability.
3. Food and Beverage Industry Storage Tank Management
The food and beverage industry requires hygienic and precise level measurement for quality control and batch consistency. Differential pressure transmitters, particularly those with sanitary connections, monitor levels in mixing tanks, fermentation vessels, and storage silos. They provide accurate data for recipe management and ensure compliance with strict hygiene standards. Their non-intrusive nature with remote seals minimizes contamination risks.
4. Pharmaceutical Process Vessel Level Measurement
In the Pharmaceutical Industries accurate and sterile level measurement is paramount for product purity and regulatory compliance. Differential pressure transmitters are used in process vessels, bioreactors, and clean-in-place (CIP) systems. Their high accuracy and ability to operate in sterile environments make them ideal for these critical applications. They support validation processes and ensure consistent batch production.

Unlock Precision with Pokcenser Automation’s Differential Pressure Solutions
Achieving precise and reliable liquid level measurement is essential for optimizing your industrial processes. At Pokcenser Automation, we specialize in providing advanced sensor technologies, including high-performance differential pressure transmitters, tailored to your specific needs. With over 10 years of expertise and a track record of 150,000+ solutions delivered globally, we are committed to helping you enhance efficiency, ensure safety, and reduce operational costs.
Contact us today to discuss your liquid level measurement challenges and discover how our certified, robust, and versatile solutions can benefit your operations. Our dedicated 6-person pre-sales and after-sales team is ready to provide comprehensive support, from initial application evaluation to seamless post-installation service. We aim for long-term partnerships and strive to create lasting value for our clients worldwide.
Phone: +86 181 7515 5326
Email: in**@*******er.com
About the Author
Li Chengxuan is a senior industrial automation expert at Pokcenser Automation, specializing in the research and application of flow, level, pressure and temperature sensors and industrial process control solutions.
FAQs
1. What is the primary difference between a differential pressure transmitter and a hydrostatic level transmitter?
A differential pressure transmitter measures the difference between two pressure points, typically the bottom and top of a tank, to determine liquid level. A hydrostatic level transmitter, often a submersible pressure sensor, measures the pressure at a single point, usually the bottom, relative to atmospheric pressure, inferring the level from that single reading. Both rely on hydrostatic principles but differ in their pressure reference points.
2. Can differential pressure transmitters be used for corrosive liquids?
Yes, differential pressure transmitters can be used for corrosive liquids. Manufacturers offer models with specialized wetted parts made from corrosion-resistant materials like Hastelloy, Monel, or PTFE. Remote seal systems further protect the transmitter by isolating it from direct contact with the corrosive medium, ensuring reliable and safe operation in aggressive chemical environments.
3. How often should a differential pressure transmitter for liquid level be calibrated?
The calibration frequency for a differential pressure transmitter depends on the application’s criticality, required accuracy, and process conditions. Generally, annual calibration is recommended. However, in highly demanding applications or those with significant temperature/pressure fluctuations, more frequent checks might be necessary to maintain optimal performance and ensure measurement integrity.
4. What are the common output signals for these transmitters?
The most common output signals for differential pressure transmitters are 4-20 mA analog signals, often with superimposed HART communication for digital data and device configuration. Other digital protocols like Modbus RTU, Foundation Fieldbus, or PROFIBUS are also widely available, enabling seamless integration with various distributed control systems (DCS) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs).
5. How does temperature affect the accuracy of liquid level measurement using differential pressure transmitters?
Temperature significantly affects accuracy by altering the liquid’s density. As temperature increases, liquid density typically decreases, leading to a lower hydrostatic pressure for the same liquid level. Conversely, a decrease in temperature increases density. Many modern differential pressure transmitters incorporate temperature compensation to correct for these density changes, ensuring accurate readings across varying process temperatures.
 English
English Spanish
Spanish
