Seamless Flow Meter Integration for Enhanced Automation Systems
You know, in the grand scheme of things, getting fluids to behave exactly as you want them to in an industrial setting isn’t just about making things run smoothly; it’s about keeping everyone safe and the whole operation from going sideways. We’ve seen firsthand how simply plugging flow meters into an automation system can turn what would otherwise be a mountain of raw, meaningless numbers into something genuinely useful. It’s about taking that data, understanding it, and then using it to tweak processes, cut down on waste, and ultimately, save a good chunk of change. This isn’t just some abstract idea; it’s about making sure every single drop, every bit of flow, actually counts towards creating a more efficient, automated environment.
Understanding the Role of Flow Meters in Modern Automation
1. The fundamental importance of accurate flow measurement
Think of accurate flow measurement as the absolute bedrock of any industrial operation that actually works. It’s not just a nice-to-have; it’s essential. This is where you get real-time snapshots of how fluids are moving, which is utterly critical for everything from keeping processes under control to guaranteeing quality and managing resources effectively. Without this precise flow data, you’re essentially flying blind. You risk all sorts of inefficiencies, your products become inconsistent, and frankly, you could be looking at some serious safety hazards. I remember this one time in a chemical plant – even tiny little changes in flow rates could completely mess up a whole batch or, even worse, cause some truly dangerous reactions. And in water treatment? Accurate flow measurement isn’t just about meeting regulations; it’s about making sure you’re adding just the right amount of chemicals, not too much, not too little. This kind of precision? It directly hits your bottom line and, let’s be honest, your environmental responsibility too.
2. How flow data drives industrial process control
If you imagine an industrial process as a living, breathing organism, then flow data is its central nervous system. It’s what keeps everything coordinated. Systems like PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), and DCS (Distributed Control Systems) all depend on this data to make smart decisions. Flow meters send their measurements straight to these control systems, which then, like a conductor with an orchestra, adjust valves, pumps, and other bits of machinery to keep everything humming along at the right parameters. This whole “closed-loop” thing means less human fiddling, more stable processes, and a system that reacts much quicker to changes. Take brewing, for example – getting consistent flow rates of ingredients is absolutely vital for a consistent product. Automated systems use flow data to manage those inputs with pinpoint accuracy.
3. Key benefits of integrating flow meters into automation systems
Bringing flow meters into your automation systems offers a whole host of perks. For starters, it supercharges process efficiency by keeping everything running at its absolute best, which means less waste and less energy consumption. When your data is more accurate, you make better decisions, and your performance metrics become far more reliable. Plus, all that automated data collection and analysis? It’s a goldmine for predictive maintenance – you can spot potential problems long before they turn into expensive breakdowns. And let’s not forget safety; seamless integration means you can react lightning-fast to any abnormal flow conditions. Ultimately, all these benefits add up to some serious cost savings and a much more reliable operation across pretty much every industry you can think of.
Technical Principles of Flow Meter Integration
1. Exploring common communication protocols for flow meters (4-20mA, Modbus RTU, HART)
When it comes to getting flow meters to play nicely with automation systems, good communication protocols are absolutely crucial. The old faithful 4-20mA analog signal is still a big player because it’s incredibly robust and doesn’t get messed up by electrical noise, even over long distances. Then there’s Modbus RTU, a serial communication protocol that’s a pretty cost-effective way to send digital data between devices and controllers. And HART (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer) protocol? That’s a clever one, combining the analog 4-20mA signal with digital communication, so you can send both process variables and diagnostic info at the same time. These protocols are what ensure reliable data exchange, which in turn allows for precise control and monitoring in industrial environments.
2. Selecting the right flow meter technology for specific automation needs
Choosing the right flow meter isn’t a one-size-fits-all situation; it really depends on what your specific application needs. Different technologies are better suited for various fluid types, flow rates, pressures, and temperatures. For instance, our PWF-U2000MCC/MCI/U1000 Ultrasonic Flowmeters are fantastic for non-invasive liquid measurements – they’re super accurate and a breeze to install. Magnetic flow meters are champions when you’re dealing with conductive liquids, while Coriolis meters give you incredibly accurate mass flow measurements for both liquids and gases. And if you’ve got clean liquids or gases where accuracy is paramount, turbine flow meters are a solid choice. Getting this selection right is key to optimal performance and making sure the thing lasts. You might find our article on Flow Meter Selection: Turbine vs. Electromagnetic vs. Ultrasonic Flow Meters pretty interesting, by the way.

3. Data acquisition and signal processing for reliable flow insights
So, you’ve got your flow meters sending out signals. What happens next? Data acquisition systems grab those raw signals and turn them into usable digital data. Then, signal processing techniques step in to clean things up – they filter out noise, compensate for environmental factors, and basically check the data’s integrity. More advanced algorithms can even spot anomalies and trends, giving you a much deeper understanding of how your process is actually behaving. This whole dance ensures that your control system gets clean, accurate, and reliable flow insights, which are absolutely critical for keeping your process stable and making smart operational adjustments. Without reliable data acquisition, you’re just asking for errors and sub-optimal control.
Practical Steps for Integrating Flow Meters into Automation Systems
1. Planning and design considerations for new and existing systems
Before you even think about plugging anything in, careful planning is the absolute first step for successful flow meter integration. Engineers need to take a good hard look at the existing infrastructure, pinpoint any potential bottlenecks, and clearly define what they want the automation system to achieve. Things like pipe size, what materials are compatible, the properties of the fluid itself, and even the environmental conditions all come into play. If you’re setting up something new, designers should pick the best spots for mounting to avoid messing with the flow and make sure it’s easy to get to for maintenance. For systems already in place, a thorough check of current instruments and control loops will tell you what’s compatible and what needs an upgrade. This proactive approach helps head off future headaches and ensures the system will last.
2. Installation best practices for various flow meter types
Getting the installation right is non-negotiable for accurate and reliable flow measurement. Every type of flow meter has its own quirks. For example, electromagnetic flow meters need a pipe that’s completely full of liquid and a decent length of straight pipe both upstream and downstream to give accurate readings. Ultrasonic flow meters, especially the clamp-on kind, demand super precise sensor placement and good contact with the pipe surface. Mechanical flow meters, like turbine or positive displacement types, need careful alignment and protection from debris. Sticking to the manufacturer’s guidelines and industry standards isn’t just a suggestion; it prevents measurement errors and helps your device live a long, happy life.
3. Configuring and calibrating flow meters for optimal performance
Configuration is basically telling the flow meter and the control system what’s what – things like pipe diameter, fluid type, and what units you want to measure in. Calibration, on the other hand, is all about making sure the flow meter is giving accurate readings by comparing its output to a known standard. You absolutely need to calibrate regularly to account for things like sensor drift, wear and tear, and changes in process conditions. This usually involves specialized calibration equipment and a strict protocol. Getting calibration right directly impacts how accurate your flow data is, which then directly affects your process control and the quality of your product.
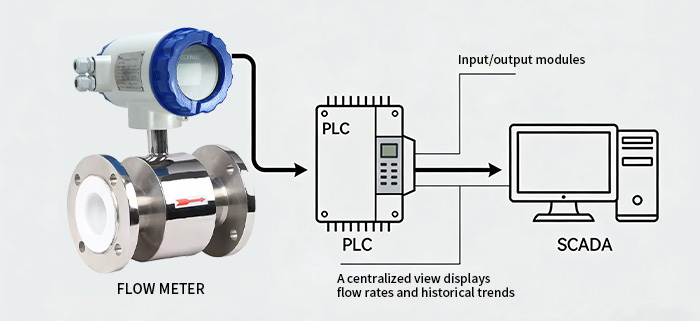
4. Integrating flow meter data with PLC, SCADA, and DCS systems
Getting flow meter data into PLCs, SCADA, and DCS systems means setting up really solid communication links. This typically involves configuring input/output modules on the PLC to receive signals from the flow meters. SCADA systems then pull this data from the PLCs, giving operators a single, centralized view of flow rates and historical trends. DCS systems take things a step further, integrating flow data into broader process control strategies, allowing for complex control algorithms and interlocks. Standardized communication protocols are the unsung heroes here, making sure data flows smoothly across the entire automation architecture.
Overcoming Challenges in Flow Meter Integration
1. Addressing compatibility issues between different devices and protocols
Oh, the joys of compatibility issues! They pop up all the time when you’re trying to integrate different devices from various manufacturers. You might have flow meters and control systems using their own proprietary communication protocols or different signal types. To get around this, engineers often resort to protocol converters or gateways – basically, translators that let incompatible systems talk to each other. Standardized protocols like Modbus RTU or HART are a huge help in bridging these gaps, ensuring smooth data exchange. A little foresight during the design phase, by specifying compatible equipment, can save a lot of headaches down the road.
2. Ensuring data integrity and cybersecurity in networked systems
In today’s industrial automation world, keeping your data intact and secure is absolutely non-negotiable. If your data gets corrupted or someone unauthorized gets access, it can completely mess up process control and lead to massive operational disruptions. That’s why you need robust cybersecurity measures – firewalls, intrusion detection systems, secure communication protocols – to protect against external threats. And within the control system itself, data validation routines are crucial for verifying that flow data is accurate and consistent, preventing bad inputs from affecting critical processes. Regular security audits and making sure your employees are trained are also key to shoring up your defenses.
3. Troubleshooting common integration problems and their solutions
You’re bound to run into common integration problems: signal loss, readings that are just plain wrong, or communication errors. Signal loss often points to wiring issues, electromagnetic interference, or a sensor that’s gone bad. Inaccurate readings? Those can come from improper calibration, a fouled sensor, or incorrect configuration settings. Communication errors usually mean there’s a mismatch in protocols or a network connectivity problem. Troubleshooting means methodically checking your wiring, verifying configurations, recalibrating sensors, and diagnosing network issues. Having good diagnostic tools and detailed system documentation makes finding and fixing these problems a whole lot quicker.
4. Implementing predictive maintenance strategies using flow data
This is where flow data really shines for predictive maintenance. By constantly keeping an eye on flow rates, pressure drops, and other related parameters, automation systems can pick up on subtle changes that hint at impending equipment failure. For instance, if you notice a gradual drop in flow rate even though your pump speed is constant, that could be a sign of pump wear or a pipe getting clogged. Analyzing historical flow data helps you establish a baseline and spot any deviations. This empowers maintenance teams to schedule interventions proactively, stopping unexpected breakdowns in their tracks and extending the life of your equipment. You might also want to check out our article on 13 Reasons Why High-Accuracy Gas Measurement with Thermal Mass Flow Meters Matters in Modern Industry.
Pokcenser’s Advanced Flow Meter Solutions for Automation
At Pokcenser Automation, we’re pretty proud of our robust and accurate flow meter solutions, all designed to slip seamlessly into all sorts of industrial automation systems. Our products are built to perform reliably across a huge range of applications, whether you’re just monitoring a simple liquid or tackling complex process control. And we don’t just sell you a product and walk away; we offer comprehensive support, from that first evaluation all the way through after-sales service, to make sure your system runs perfectly.
1. Enhancing process control with LZS Series Plastic and LZ Metal Tube Flow Meters
Our LZS Series Plastic Tube Flowmeter is a fantastic, lightweight, corrosion-resistant option for straightforward liquid flow monitoring. The clear design means you can easily see what’s going on and get accurate readings. But for those tougher jobs, our LZ Metal Tube Flow Meter really steps up, offering rugged performance in high-temperature, high-pressure, and corrosive environments. Both series integrate effortlessly into existing systems, feeding you crucial flow data to really boost your process control. These meters are perfect for a variety of industries, including chemical, pharmaceutical, and water treatment.

2. Achieving precision with PWF-U2000MCC/MCI/U1000 Ultrasonic Flowmeters
When it comes to precision, our PWF-U2000MCC/MCI/U1000 Ultrasonic Flowmeters really deliver. They offer high-accuracy, non-invasive flow measurement. The PWF-U2000MCC is a multi-channel clamp-on unit, great for both industrial and municipal water applications. If you need insertion-type measurement without tearing up your pipelines, the PWF-U2000MCI is your go-to. And for those smaller pipes, the PWF-U1000 offers quick, non-invasive installation. These [Ultrasonic Flow Meters]( are incredibly versatile, handling various liquid types and even offering optional temperature and pressure integration for a truly comprehensive picture. Their advanced signal processing ensures you get reliable data, even when conditions are challenging.
3. Integrating specialized sensors for comprehensive system monitoring (TDS, pH, DO, Level)
We don’t just stop at flow measurement. Pokcenser Automation also offers a whole range of specialized sensors to give you a complete overview of your system. Our PT6500 Online TDS Meter Controller and PCS3740PCD Digital Conductivity TDS Salinity Sensor ensure you’re accurately monitoring water quality. The PCS1753CD Plastic pH Sensor and PCS2700CD Digital ORP Sensor provide precise pH and ORP measurements. And for keeping tabs on levels, we’ve got various solutions, including our PWL-U201/PWL-U202 Ultrasonic sensors and PWP412-T3 submersible level transmitters. All these sensors integrate seamlessly, giving you a full, clear picture of your process conditions.
4. Custom solutions and OEM/ODM capabilities for unique industrial requirements
We get it – every industrial application has its own quirks and challenges. That’s why Pokcenser Automation offers custom solutions and OEM/ODM capabilities to meet those unique client needs. Our experienced team works hand-in-hand with customers to design and manufacture bespoke flow meters and sensors, ensuring perfect compatibility and optimal performance for specialized requirements. This flexibility allows us to tackle even the most complex integration scenarios and deliver tailored solutions that genuinely enhance automation systems. Ultimately, we’re committed to creating real value for our clients, wherever they are in the world.
Partner with Pokcenser Automation for Seamless Integration
Ready to really boost the efficiency and reliability of your industrial processes? Partner with Pokcenser Automation. Our advanced flow meter solutions, backed by our deep expertise in industrial process control automation, guarantee seamless integration and optimal performance for your systems. Don’t hesitate to reach out today to chat about your specific requirements and discover how our tailored solutions can genuinely improve your operations.
Phone: +86 181 7515 5326
Email: in**@*******er.com
About the Author
Li Chengxuan is a senior industrial automation expert at Pokcenser Automation, specializing in the research and application of flow, level, pressure and temperature sensors and industrial process control solutions. With over a decade of experience, Li Chengxuan is dedicated to advancing industrial efficiency and reliability through innovative sensor technologies and seamless system integration.
FAQs
1. What are the primary communication protocols used for flow meter integration in automation systems?
Well, when we’re talking about getting flow meters to integrate smoothly into automation systems, the main communication protocols you’ll encounter are 4-20mA, Modbus RTU, and HART. The 4-20mA is an analog current loop – it’s really robust and doesn’t get much interference from electrical noise, which is great for data transmission. Modbus RTU is a serial digital protocol, offering a pretty cost-effective way to exchange data. And HART? That one’s clever, combining both analog and digital signals, so you can transmit both the process variable and diagnostic information at the same time. These protocols are what ensure your data flows reliably to your control systems.
2. How does flow meter integration contribute to predictive maintenance in industrial settings?
Flow meter integration is a huge player in predictive maintenance because it gives you continuous, real-time data about how fluids are behaving. By analyzing this data, you can spot abnormal patterns or deviations from what’s considered normal performance, which can be an early warning sign of equipment degradation. For instance, if you see a change in flow rate or a pressure drop, it might indicate pump wear or a blockage in a pipe. This allows maintenance teams to step in proactively, preventing unexpected failures and significantly reducing downtime.
3. What types of flow meters are best suited for integration into harsh industrial environments?
For those really tough industrial environments, you’ll generally want to look at robust flow meters like our LZ Metal Tube Flow Meters or certain electromagnetic flow meters. These are built to last, with durable construction, resistance to high temperatures and pressures, and materials that can stand up to corrosive substances. Our Ultrasonic Flow Meters with IP68-rated sensors also perform exceptionally well in challenging conditions, giving you reliable measurements without direct contact with aggressive fluids.
4. Can Pokcenser Automation provide customized flow meter solutions for specific integration challenges?
Absolutely, yes! At Pokcenser Automation, we pride ourselves on offering customized flow meter solutions and OEM/ODM capabilities. We make it a point to work very closely with our clients to truly understand their unique industrial requirements. Then, we design tailored products that integrate perfectly into their existing automation systems. Our whole goal is to address those specific challenges, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency for specialized applications.
5. What are the key considerations for ensuring data accuracy when integrating flow meters?
Ensuring data accuracy when integrating flow meters really boils down to a few key things. First off, picking the right flow meter technology for your specific application is fundamental. Then, proper installation, strictly following the manufacturer’s guidelines, is crucial for minimizing measurement errors. Regular calibration against known standards is also essential to account for any drift and maintain precision over time. And finally, having robust signal processing and data validation within your automation system helps filter out noise and verifies the integrity of your data.
 English
English Spanish
Spanish
