How do Magnetostrictive Sensors Work?
Accurate and reliable measurement is at the heart of modern industrial automation. From monitoring fluid levels in storage tanks to tracking hydraulic cylinder displacement and ensuring safety in oil and gas operations, industries depend on technologies that combine high accuracy, robustness, and long service life. One of the most trusted solutions in this area is the magnetostrictive sensor. Known for its non-contact design and excellent repeatability, magnetostrictive position sensors and magnetostrictive level sensors play vital roles wherever precision measurement is non-negotiable.
Understanding Magnetostrictive Sensor
A magnetostrictive sensor is a device designed to measure linear displacement, level, or position with remarkable accuracy. The underlying principle is the magnetostrictive effect—the slight change in shape that ferromagnetic materials experience when exposed to a magnetic field.
In practical terms, the magnetostrictive position sensor consists of a waveguide, a position magnet, a pickup coil, and electronic circuitry. A short current pulse travels through the waveguide, creating a magnetic field that interacts with the permanent magnetic field of the float or position magnet. This interaction produces a torsional strain wave that moves along the waveguide until it reaches the pickup coil, where it is detected. The time difference between the initial pulse and the arrival of the wave corresponds directly to the exact position of the magnet. Because magnetostrictive displacement sensors rely on time-of-flight rather than signal strength, the result is both absolute and highly stable, even under changing operating conditions.
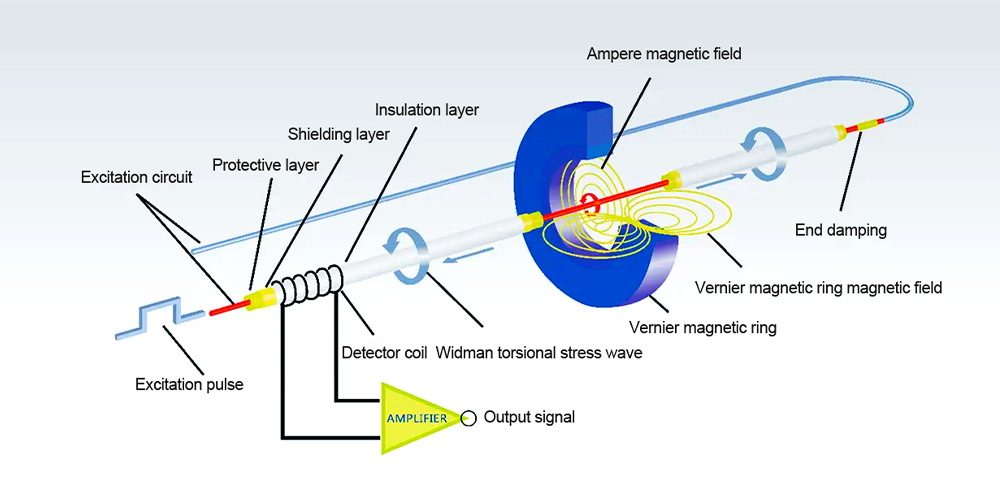
Figure 1. Principle of magnetostrictive sensing — an excitation pulse generates a torsional stress wave along the waveguide, detected by coil and magnetic field interaction.
Why Magnetostrictive Position Sensors Deliver High-Accuracy Measurements
One of the biggest strengths of magnetostrictive sensor technology is its precision. Industrial magnetostrictive sensors typically reach accuracy of ±0.01% of the full measurement range, with resolutions in the micron level. Unlike incremental encoders that lose position data when power is lost, magnetostrictive sensors provide absolute position feedback, meaning they always know their measurement reference as soon as power returns.
Equally important is their non-contact design. Since the float or magnet does not physically touch the waveguide in a magnetostrictive level sensor, there is no mechanical wear, ensuring extremely long lifespans—often more than a decade of continuous operation. These non-contact linear displacement sensors also perform reliably in environments with high vibration, shock, pressure, or temperature, making them ideal for industries where downtime is costly.
In addition, magnetostrictive level transmitters and magnetostrictive displacement sensors are available with a wide range of communication options, from traditional analog signals to modern industrial protocols like Modbus, Profibus, EtherCAT, and CANopen, which allows seamless integration into existing control systems.
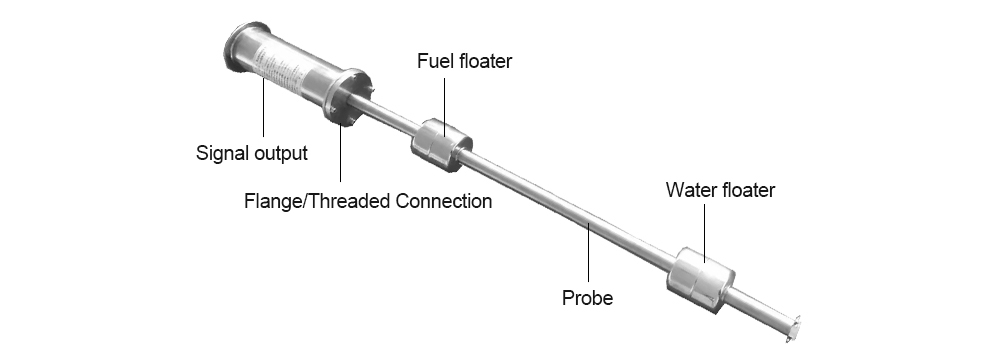
Figure 2. Internal structure of a magnetostrictive level sensor — including probe, floaters, and output interface for dual-phase level detection.
Applications of Magnetostrictive Sensors Across Industries
Magnetostrictive sensors are widely used wherever accurate position or level measurement is required. In the oil and gas industry, magnetostrictive level sensors are trusted for storage tank monitoring, custody transfer, and leak detection. Their ability to withstand harsh conditions makes industrial magnetostrictive sensors indispensable for monitoring crude oil, LNG, and refined fuels.
In the chemical sector, magnetostrictive level transmitters with corrosion-resistant stainless steel probes provide reliable monitoring in aggressive environments, ensuring safety and process stability when dealing with solvents and acids.
Power generation plants rely on magnetostrictive position sensors for turbine monitoring, valve position tracking, and boiler water level control, where accuracy directly impacts efficiency and safety.
In water and wastewater management, magnetostrictive level sensors ensure precise monitoring of reservoirs, pumping stations, and treatment facilities, even when foam, vapor, or turbulence would disrupt ultrasonic or radar sensors.
The food and beverage industry uses hygienic versions of magnetostrictive sensors for applications like milk storage, beverage production, and CO₂ dosing. Their non-contact measurement ensures sanitary operation without risk of contamination.
Magnetostrictive displacement sensors are also integral to hydraulic and pneumatic systems, where they provide feedback on cylinder position in construction equipment, injection molding machines, and presses. Even in emerging fields like renewable energy, magnetostrictive position sensors are being adopted for monitoring hydraulic actuators in solar panels and pitch control in wind turbines.

Figure 3. Real-world installation of PokcenserTech magnetostrictive level transmitters in industrial process systems for accurate liquid level measurement.
Comparing Magnetostrictive Sensors with Other Measurement Technologies
While many sensor types are available, magnetostrictive sensor technology stands out for its unique combination of precision and durability. Unlike potentiometers, magnetostrictive sensors have no moving parts to wear out. Compared to ultrasonic sensors, magnetostrictive level sensors are unaffected by surface turbulence, foam, or vapor. Capacitive and optical sensors often suffer from contamination, while industrial magnetostrictive sensors continue working reliably even in dirty or oily conditions. Float switches can only provide point-level detection, but magnetostrictive level transmitters deliver continuous, real-time measurement with absolute position measurement capabilities.
Factors That Influence Magnetostrictive Sensor Measurement Accuracy
Like any technology, magnetostrictive position sensors require proper installation and calibration to perform at their best. Temperature extremes can slightly affect the speed of sound in the waveguide, while strong external electromagnetic fields may interfere with signals if grounding is poor. Misaligned installation or contaminated floats can also reduce accuracy in magnetostrictive level sensors. However, when properly installed and regularly maintained, these high-accuracy measurement sensors consistently deliver industry-leading precision.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices for Magnetostrictive Sensors
To maximize reliability, magnetostrictive sensors should be mounted vertically in tanks or aligned correctly with hydraulic cylinders. Proper electrical grounding is essential to minimize interference with magnetostrictive displacement sensors. Annual calibration is recommended for critical applications using magnetostrictive level transmitters, while periodic inspections ensure that floats remain clean and free from buildup. Many modern industrial magnetostrictive sensors also include built-in diagnostic functions that provide real-time feedback on sensor health, making maintenance more proactive.

Figure 4. Field application of a magnetostrictive level transmitter integrated into a process control system, ensuring continuous and precise monitoring.
The Future of Magnetostrictive Sensor Technology
As industries transition into the era of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0, magnetostrictive sensors are evolving too. New models of magnetostrictive position sensors feature IoT connectivity, enabling wireless data transfer and integration into cloud platforms. With self-diagnostic and predictive maintenance capabilities, these non-contact linear displacement sensors can detect performance drift before it impacts production. Miniaturized magnetostrictive displacement sensors are making their way into robotics, medical devices, and electric vehicles, while energy-efficient electronics are opening opportunities for battery-powered and remote monitoring applications using magnetostrictive level sensors.
If your business depends on high-accuracy position measurement or liquid level monitoring, magnetostrictive sensors offer the reliability and precision you need. Whether you require magnetostrictive level sensors for tank monitoring or magnetostrictive position sensors for hydraulic applications, these industrial magnetostrictive sensors reduce downtime, support compliance, and ensure long-term savings.
Contact our team today to request a demo or consultation and discover how our magnetostrictive sensor solutions can optimize your operations.
FAQs About Magnetostrictive Sensors
Q: What can magnetostrictive sensors measure?
A: Magnetostrictive level sensors and magnetostrictive position sensors can measure liquid levels, hydraulic displacement, chemical storage tanks, and industrial cylinders with exceptional precision.
Q: How accurate are magnetostrictive sensors?
A: Magnetostrictive displacement sensors typically offer accuracy up to ±0.01% of the full measurement range, with resolution in the micron scale.
Q: Are magnetostrictive sensors suitable for hazardous environments?
A: Yes, ATEX- and IECEx-certified versions of industrial magnetostrictive sensors are available for use in explosive atmospheres.
Q: What is the typical lifespan of a magnetostrictive sensor?
A: Because magnetostrictive position sensors operate without contact or wear, service life often exceeds 10 years.
Q: Which industries benefit most from magnetostrictive sensor technology?
A: Oil and gas, chemical, power generation, water treatment, food and beverage, hydraulic systems, and renewable energy are among the largest users of magnetostrictive level sensors and magnetostrictive position sensors.
Keywords
magnetostrictive sensor, magnetostrictive level sensor, magnetostrictive position sensor, magnetostrictive displacement sensor, industrial magnetostrictive sensor, non-contact linear displacement sensor, high-accuracy measurement sensor, liquid level transmitter, absolute position measurement, magnetostrictive technology, magnetostrictive sensor technology, magnetostrictive level transmitter
 English
English Spanish
Spanish
