Gas Pressure Sensors: Applications, Selection, and Best Practices
You know, when you think about it, gas pressure sensors are really the unsung heroes of so many industries. They’re tucked away in countless industrial and scientific setups, quietly doing their job, providing the kind of essential data that keeps everything running smoothly, safely, and efficiently. Getting pressure measurements right isn’t just about numbers; it’s about making sure systems don’t fail and that everything performs at its best. For engineers and technicians across the board, truly grasping the different types, where they fit in, and how to use them properly isn’t just helpful – it’s absolutely crucial. My goal here is to share some comprehensive insights to help you cut through the noise and make truly informed decisions.
Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Gas Pressure Sensors
At its heart, a gas pressure sensor is a pretty clever device: it takes the physical force of gas pressure and turns it into an electrical signal. That signal then gets crunched, either to show you a reading on a screen or to tell a system what to do. While the exact “how” changes depending on the sensor’s design, the core mission is always the same: give us reliable and accurate measurements.
1. Defining Gas Pressure and Its Measurement
Think of gas pressure as the collective push of all those tiny gas particles against a surface, spread out over a certain area. It’s a foundational concept in so many processes, and getting its measurement right is absolutely non-negotiable for safety, quality control, and just making sure things run as they should. We usually talk about pressure in terms like Pascals (Pa), pounds per square inch (psi), or bar – just different ways of quantifying that same fundamental push.
2. Exploring Different Types of Gas Pressure Sensors
It’s fascinating how many ways there are to skin this cat! Various technologies have popped up over the years, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Piezoresistive Sensors: These are quite common. They work by noticing a change in electrical resistance when a material gets stressed mechanically. Often, you’ll find these are Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors made of silicon. They’re real workhorses, offering high accuracy and reliability, especially when you’re looking at both steady (static) and changing (dynamic) pressures.
- Capacitive Sensors: Imagine two tiny plates, and one of them is a flexible diaphragm. When pressure hits that diaphragm, it bends, changing the distance between the plates, and that change in distance alters the capacitance. That’s how these devices measure pressure. They’re loved for their super high sensitivity and how incredibly stable they are over the long haul.
- Electromagnetic Sensors: While you won’t typically see these directly measuring gas pressure in most everyday scenarios, there are specialized electromagnetic principles that come into play for specific situations, particularly when you’re trying to figure out pressure drops related to flow.
- Thermal Sensors: These clever sensors gauge pressure based on how well a gas conducts heat – and that conductivity changes with pressure. You’ll often find them doing duty in vacuum measurements.
- Optical Sensors: Here, we’re talking about light! Optical fibers or other optical bits detect changes in light properties that are caused by pressure. A huge plus for these is their immunity to electromagnetic interference, and they can really shine in some seriously nasty environments.
- Piezoelectric Sensors: These guys generate an electrical charge when you apply mechanical stress. Because they react so quickly, they’re absolutely perfect for measuring dynamic pressures – think sudden, rapid changes.

3. Key Performance Parameters for Gas Pressure Sensors
Picking the right gas pressure sensor isn’t like grabbing a loaf of bread; it requires a bit of thought, especially about a few crucial performance metrics.
- Accuracy: This is pretty straightforward: how close is the sensor’s reading to the actual value? We usually express it as a percentage of the sensor’s full output range.
- Range: This simply tells you the lowest and highest pressure values the sensor can reliably measure.
- Resolution: Think of this as the sensor’s “fineness of detail” – the tiniest change in pressure it can actually pick up.
- Repeatability: If you give the sensor the exact same pressure under the exact same conditions, will it give you the exact same reading every single time? That’s repeatability.
- Stability: Can the sensor keep performing well over time and even when its surroundings change? That’s its stability.
- Response Time: How quickly does the sensor react to a pressure change and give you a correct reading? Crucial for dynamic systems!
- Temperature Compensation: Let’s be real, temperature can mess with readings. Many sensors have built-in smarts to correct for these temperature-induced errors, which is absolutely vital for accuracy in environments where the temperature is all over the place.
- Overpressure Capability: This is a big one for safety: what’s the absolute maximum pressure the sensor can handle without getting permanently damaged?
Diverse Applications of Gas Pressure Sensors Across Industries
It’s hard to overstate how vital gas pressure sensors are. They pop up in so many industries, not just making sure things are safe, but also fine-tuning processes and generally making operations more efficient.
1. Gas Pressure Sensors in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production
In the rough-and-tumble world of oil and gas, these sensors are absolutely critical. They’re constantly keeping an eye on wellhead pressure, making sure pipelines aren’t springing leaks, and checking levels in storage tanks. They’re the silent guardians preventing spills, helping us get the most out of extraction, and ensuring hydrocarbons get transported safely. For example, you’ll find high-pressure sensors watching over drilling, and in those truly explosive atmospheres, hazardous area sensors are simply non-negotiable.
2. Utilizing Gas Pressure Sensors in Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
If you’ve ever been near a Chemical or petrochemical plant, you know precision is everything. They absolutely depend on accurate pressure control to get reactions just right and, more importantly, to keep everyone safe. Gas pressure sensors are constantly monitoring reactors, distillation columns, and storage tanks, making sure processes stay within safe boundaries. They’re essential for handling corrosive gases and maintaining super strict quality control. This includes keeping a close watch on pressure in Chemical Tanks.
3. The Role of Gas Pressure Sensors in HVAC and Building Management Systems
Even in our homes and offices, HVAC systems lean on gas pressure sensors. They’re monitoring refrigerant lines, checking duct pressure, and making sure fans are doing their job. These sensors are what ensure everything runs efficiently, keeps energy consumption down, and maintains that comfortable indoor air quality we all appreciate. They’re also pretty good at sniffing out blockages or leaks before they become big problems. These applications, by the way, are a big part of broader Environmental Monitoring efforts.
4. Gas Pressure Sensor Applications in Medical Devices and Healthcare
In the medical world, where lives are literally on the line, miniature gas pressure sensors are embedded in devices like respirators, anesthesia machines, and blood pressure monitors. They’re giving doctors real-time data for patient monitoring and making sure medications are delivered with pinpoint accuracy. Here, accuracy and reliability aren’t just good features; they’re absolutely paramount. The Pharmaceutical Industries also use these sensors extensively, as you might imagine.
5. Environmental Monitoring and Weather Forecasting with Gas Pressure Sensors
Ever wonder how weather stations get their data? Gas pressure sensors are a huge part of it, integrated into weather stations and Environmental Monitoring systems. They measure atmospheric pressure, feeding crucial data into weather forecasting and climate research. High-precision sensors can even pick up the most subtle atmospheric shifts, leading to much more accurate predictions.
6. Industrial Automation and Process Control Using Gas Pressure Sensors
In the realm of industrial automation, gas pressure sensors are foundational. They’re controlling pneumatic systems, guiding robotic arms, and overseeing manufacturing processes. They provide the feedback loops for automated control, ensuring precise movements and consistent product quality. When integrated into smart systems, they really boost overall efficiency.
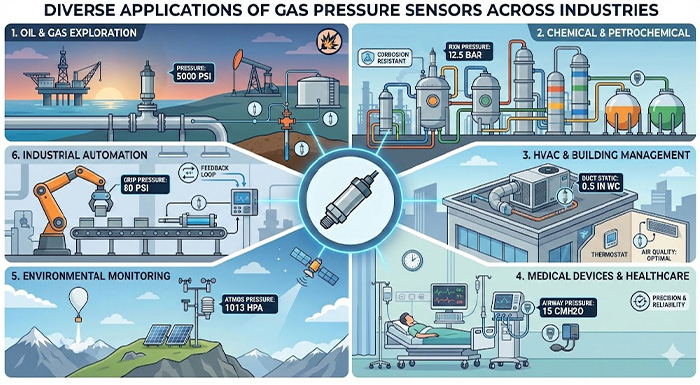
Essential Tips for Selecting the Right Gas Pressure Sensor
Honestly, choosing the right gas pressure sensor is a big deal. It directly impacts how well your process runs, how safe it is, and even your long-term costs. There are quite a few things to chew on when making this decision.
1. Matching Sensor Type to Specific Application Requirements
First things first, you’ve got to really understand what your application needs. What kind of gas are you dealing with? What’s the pressure range? What about temperature and environmental conditions? For instance, if you’re working with corrosive gases, you absolutely need sensors made with materials that can handle them.
| Sensor Type | Best Suited For | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Piezoresistive | General industrial, automotive, medical | High accuracy, robust, cost-effective |
| Capacitive | Low pressure, high sensitivity, stable | High sensitivity, excellent long-term stability |
| Piezoelectric | Dynamic measurements, high-frequency response | Fast response, wide dynamic range |
| Thermal | Vacuum, low pressure, gas composition analysis | High sensitivity at low pressures |
| Optical | Harsh environments, EMI immunity | EMI immunity, high temperature resistance |
2. Considering Environmental Factors and Operating Conditions
The environment a sensor lives in can really make or break its performance. High temperatures, humidity, vibrations, or corrosive substances can all mess with accuracy and shorten its life. So, you need to pick sensors with the right IP ratings and materials that can stand up to those conditions. For example, in places where explosions are a risk, explosion-proof sensors aren’t just a good idea; they’re a necessity.
3. Evaluating Accuracy, Range, and Long-Term Stability
When you’re looking at your application’s most critical needs, accuracy and stability should be at the top of your list. Sure, a super-accurate sensor might cost a bit more upfront, but it could be absolutely essential for precise control. And good long-term stability means you won’t be constantly recalibrating, which saves a ton on maintenance.
4. Understanding Output Signals and Communication Protocols
Sensors usually talk to other systems either through analog signals (like 4-20 mA or 0-10V) or digital ones (think RS485 Modbus or HART). You need to make sure the output signal you choose plays nicely with your existing control system. Digital protocols, by the way, often give you better data integrity and more diagnostic information, which is a nice bonus.
5. The Importance of Certifications and Compliance Standards
Never overlook this one: make sure your sensor meets all the relevant industry standards and certifications. This could mean safety certifications like ATEX for dangerous environments or specific medical device standards. Compliance isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about guaranteeing reliability and, most importantly, safety.
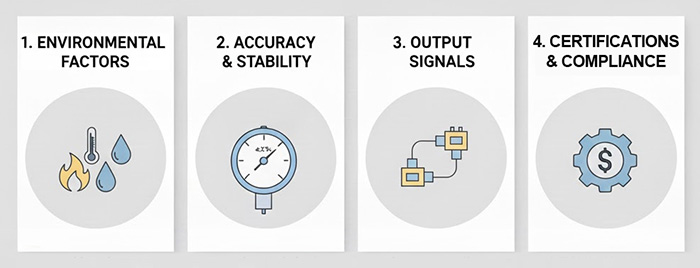
Best Practices for Installation, Calibration, and Maintenance of Gas Pressure Sensors
To get the most out of your sensor – maximum performance and a really long life – you’ve got to get the installation right, calibrate it regularly, and keep up with diligent maintenance.
1. Proper Installation Techniques to Ensure Optimal Performance
- Mount that sensor securely! You want to keep vibration effects to a minimum.
- Pay attention to the manufacturer’s instructions for orientation. It matters.
- Use the right fittings and sealing materials. Leaks are a no-go.
- Protect your investment from physical damage and extreme conditions.
- Route those cables carefully to avoid any electromagnetic interference.
2. Regular Calibration Procedures for Maintaining Accuracy
Think of calibration as a regular health check for your sensor. It’s absolutely essential to keep it accurate over time.
- Set up a calibration schedule. The manufacturer’s recommendations are a good start, but also consider how critical your application is.
- Always use certified calibration equipment and standards that can be traced back to a national standard.
- Try to calibrate the sensor in conditions that are as close as possible to its actual operating environment.
- Adjust the sensor’s output based on what your calibration results tell you.
- Keep meticulous records of all your calibration data – it’s key for compliance and just knowing your sensor’s history.
3. Troubleshooting Common Issues with Gas Pressure Sensors
You’ll inevitably run into issues like readings that just don’t seem right, no output at all, or signals that come and go.
- Start with the basics: check the power supply and all your electrical connections.
- Look for any physical damage or blockages in the pressure lines.
- Double-check that the sensor is configured and scaled correctly.
- Test for any electromagnetic interference that might be throwing things off.
- If accuracy seems to be drifting, it’s probably time for a recalibration.
4. Implementing Effective Maintenance Schedules for Longevity
Being proactive with maintenance is the best way to prevent failures and keep things running without interruption.
- Make it a habit to regularly clean the sensor and its pressure ports.
- Inspect for any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage to any parts.
- If you find worn-out parts or seals, replace them immediately.
- If there’s a firmware update available, install it. It can often boost performance.
- And again, keep detailed maintenance records. They’re invaluable.
The Future of Gas Pressure Sensing Technology and Innovations
It’s a dynamic field, this gas pressure sensing! It’s constantly pushing forward, driven by the never-ending quest for better accuracy, smaller sizes, and seamless connectivity.
1. Advancements in Miniaturization and Wireless Connectivity
Smaller sensors mean they can be crammed into tinier devices and used in more remote places. And wireless connectivity? That’s a game-changer. It means you can collect data from spots that are tough to reach or from mobile equipment, cutting down on wiring headaches and installation costs.
2. Integration with IoT and Smart Industrial Systems
More and more, gas pressure sensors are becoming part of the Internet of Things (IoT) and those clever smart industrial systems. This opens up a world of real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance (fixing things before they break!), and much smarter automation. These smart sensors can even talk directly to cloud platforms, letting you monitor and control things from anywhere.
3. Emerging Materials and Manufacturing Techniques
There’s some really exciting research happening with new materials – graphene and advanced ceramics, for instance. These promise sensors that are even more sensitive, tougher, and can stand up to even harsher environments. And with advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing, we’re seeing complex sensor designs and custom solutions that just weren’t possible before.
Partner with Pokcenser Automation for Your Gas Pressure Sensing Needs
Look, choosing the right gas pressure sensor isn’t just another item on a checklist. It’s a critical decision that directly impacts how efficient your processes are, how safe your operations remain, and ultimately, your bottom line. Here at Pokcenser Automation, we’re not just selling products; we specialize in delivering top-tier pressure transmitters and comprehensive industrial process control solutions. Our expertise means you’re not just getting a sensor; you’re getting a reliable, accurate, and durable solution perfectly matched to your specific application. Don’t hesitate – reach out to us today. Let’s talk about what you need and explore how our solutions can truly elevate your operations.
Phone: +86 181 7515 5326
Email: in**@*******er.com
FAQs
1. What is the primary difference between absolute, gauge, and differential pressure sensors?
Alright, let’s break this down. An absolute pressure sensor measures pressure against a perfect vacuum – zero pressure – so it gives you the true, total force. A gauge pressure sensor, on the other hand, measures pressure relative to the surrounding atmospheric pressure; it’s essentially telling you how much above or below ambient pressure you are. And then there’s the differential pressure sensor, which is a bit different. It measures the difference between two separate input pressures, and you’ll often see these used for things like measuring flow rates or checking if a filter is clogged.
2. How often should gas pressure sensors be calibrated?
That’s a great question, and the answer isn’t a simple one-size-fits-all. It really depends on a few things: how critical your application is, the kind of environment the sensor is in, and what the manufacturer suggests. If you’re in a high-accuracy situation or a particularly harsh environment, you might need to calibrate every 6-12 months. For less critical applications, you might be able to stretch that out to 1-2 years.
3. Can gas pressure sensors be used in hazardous environments?
Absolutely, yes! In fact, many gas pressure sensors are specifically engineered for hazardous environments. You’ll typically find them with certifications like ATEX or IECEx, which basically tell you they’re either intrinsically safe (meaning they can’t generate enough energy to cause an explosion) or explosion-proof (designed to contain an explosion if one occurs). The key is to make sure you select a sensor that’s specifically rated for the hazardous classification of your particular environment.
4. What factors influence the accuracy of a gas pressure sensor?
Oh, quite a few things can throw off a sensor’s accuracy! Temperature swings are a big one, as are vibrations, electromagnetic interference, and the natural drift that sensors experience over time. Even the quality of the initial calibration plays a huge role. The good news is that with proper installation, controlling the environment as much as possible, and regular calibration, you can significantly reduce these effects.
5. How do I choose the correct pressure range for my application?
When picking a pressure range, you want one that comfortably covers your expected operating pressure, plus a little extra wiggle room for any overpressure situations. Ideally, your normal operating pressure should fall somewhere between 20% and 80% of the sensor’s full-scale range – that’s usually where they’re most accurate. The trick is to avoid a range that’s either way too wide (you lose resolution) or too narrow (you risk damaging the sensor).
About the Author
Li Chengxuan is a senior industrial automation expert at Pokcenser Automation, specializing in the research and application of flow, level, pressure and temperature sensors and industrial process control solutions.
 English
English Spanish
Spanish
